Acute COPD exacerbation despite triple inhaled therapy: a molecular insight – TripleEx study
N.A. Sievi, F. Schmidt, K. Fricke, D.M. Baur, S. Basler, J. Herth, M. Kohler
Breath metabolomics in COPD exacerbations
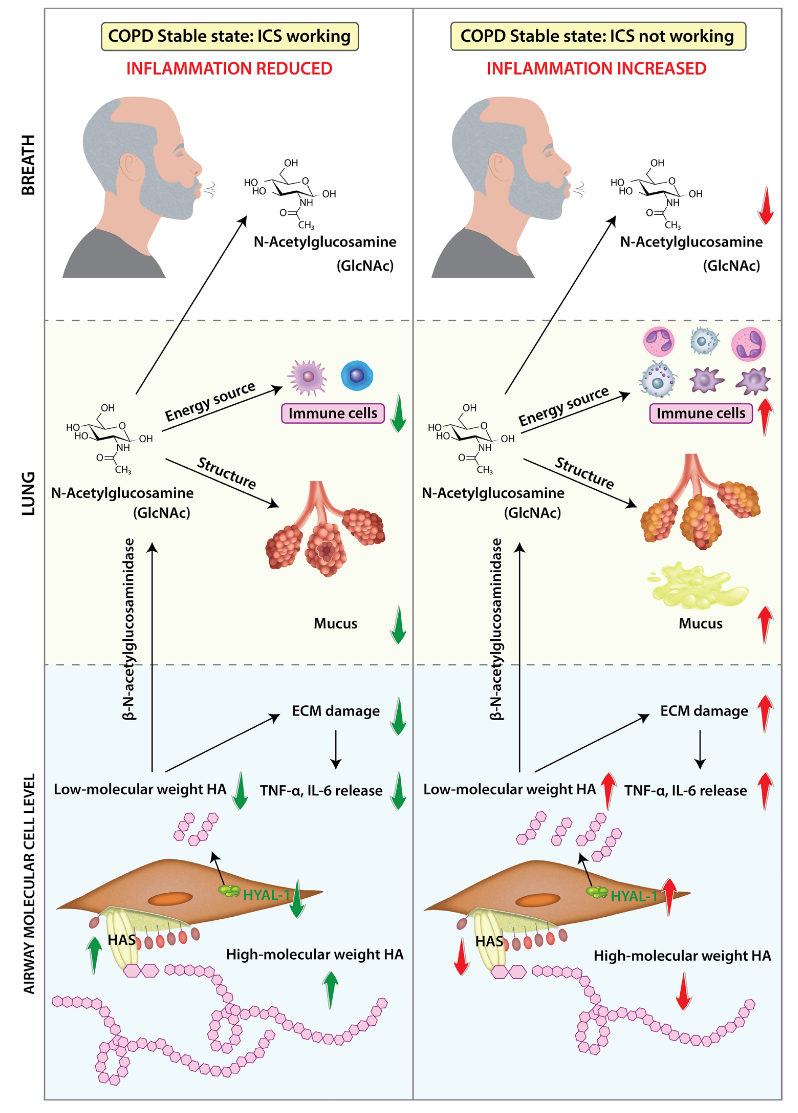
This study examined whether real-time breath analysis can detect metabolic changes during acute exacerbations of COPD (AECOPD) compared to the stable state in patients receiving triple inhaled therapy. Breath profiles from 28 patients revealed alterations in aminosugar, linoleate, and butanoate pathways. A prediction model discriminated AECOPD from stable state with high accuracy (AUC = 0.84, sensitivity and specificity 86%). These findings suggest that exhaled breath analysis may provide a rapid, non-invasive tool for detecting exacerbations and reveal aminosugar metabolism as a potential therapeutic target.
Metabolite Fusion between Breath and Blood Enables More In-Depth Understanding of the Endogenous Metabolome
Z. Tang, J. Yang, B. Su, X. Xu, X. Luo, H. Wang, K. Zhang, T. Huan, P. Sinues, M. Fang, X. Li
Breath Metabolomics Beyond Blood
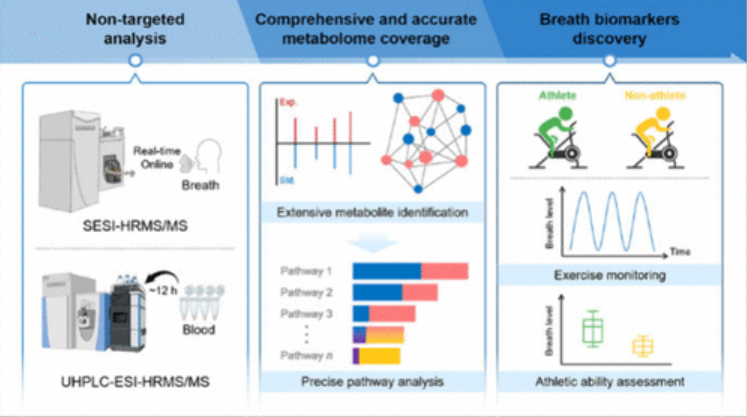
This study demonstrates how exhaled breath can complement blood in metabolomics by retaining volatile compounds often lost in blood analysis. Researchers combined a controlled exercise protocol, a custom breath metabolomics database, and metabolite fusion across breath and blood to boost identification accuracy. High-resolution MS revealed 66 unique breath metabolites, 59 unique blood metabolites, and only 4 shared. Integrating both matrices expanded pathway coverage and highlighted breath-specific markers of exercise-induced changes, paving the way for novel biomarkers and future smart wearable applications.
Exploring exhaled breath biomarkers for lactose intolerance diagnosis: the Lactobreath pilot study protocol
S. Giannoukos, K. J.e Burton-Pimentel, R. Guillod, G. Vergères, D. Pohl
The Lactobreath study explores real-time breath analysis as a novel, non-invasive tool to detect lactose intolerance. In this double-blind trial, 120 participants undergo postprandial testing with lactose or glucose. Using Super SESI-HRMS, the study captures detailed exhalome profiles and correlates them with symptoms, hydrogen levels, gut transit (via ingestible gas capsules), bowel sounds, urine metabolites, and genetic markers. This integrative approach aims to move beyond standard hydrogen breath tests and validate molecular breath signatures as clinical biomarkers for food intolerance.
Smell of stress: An in-depth look into the Bacillus subtilis 168 volatilome during pH stress using secondary electrospray ionization-Orbitrap mass spectrometry
H. G. Mengers, F. Völker, L. M. Blank
Decoding Bacillus subtilis’ Volatilome Under Acid Stress, in Real Time with SESI-Orbitrap
This study reveals the acid stress volatilome of Bacillus subtilis using real-time SESI-Orbitrap MS, offering unprecedented temporal resolution (0.3 Hz) during pH shock in resting cells. Over 450 compounds were tracked across 16,000 data points, uncovering both immediate and delayed VOC responses. Acetoin dominated, as expected, but a novel signal (C₄H₆O) also emerged. This work highlights SESI’s power to monitor microbial stress responses via off-gas VOCs, non-invasively, instantly, and at the molecular scale.
Temperature Programming Secondary Electrospray Ionization (TP-SESI): A Novel Approach for Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Plant Volatile Organic Compounds
S.M. Ashbacher D.C. Muddiman
Heat-Stress VOC Profiling in Basil Using TP-SESI
This study showcases temperature-programmed secondary electrospray ionization (TP-SESI) as a powerful tool for probing plant responses to heat stress. By applying controlled heating to Ocimum basilicum leaves, TP-SESI enabled real-time, non-destructive monitoring of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The results revealed clear, temperature-dependent changes in VOC composition and abundance, offering insights into thermal stress signaling pathways. TP-SESI emerges as a sensitive, orthogonal method for exploring plant resilience mechanisms and stress-induced metabolism.
Exploring breath metabolomics as a non-invasive tool for detecting pulmonary vascular disease
S. Basler, K. Fricke, N.A. Sievi1, A. Arvaji, F.Schmidt, J. Herth, D.M. Baur, M.Kohler, S.Ulrich, and M. Lichtblau
Breath metabolome profiling for pulmonary vascular disease detection
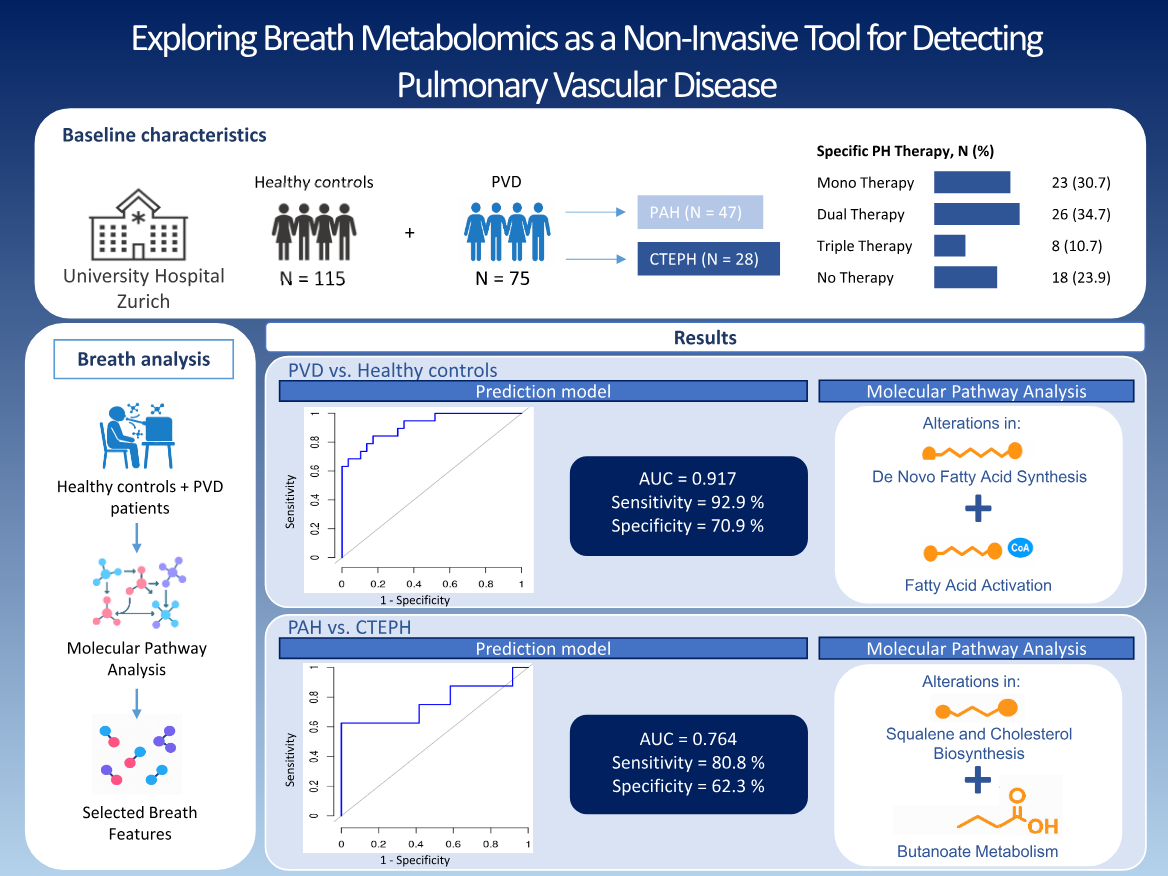
This study evaluated whether real-time breath analysis could identify metabolic differences between patients with pulmonary vascular disease (PVD) and healthy controls, and distinguish between two major subtypes: pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH). Using metabolomic prediction models, breath profiles from 75 patients and 115 controls were compared. The models achieved high accuracy in detecting PVD (AUC = 0.917) and moderate accuracy in differentiating PAH from CTEPH (AUC = 0.764). Pathway analysis revealed alterations in fatty acid metabolism. These findings highlight the potential of breath analysis as a non-invasive, real-time diagnostic tool for early detection and subtype differentiation in PVD.
A sampling method for differentiating breath and ruminal exhaled volatile organic compounds in dairy cows using methane as a marker
M.A. Barrientos-Blanco, U. Arshad, S. Giannoukos, M.Z. Islam, C. Kunz, R. Peng, S.E. Räisänen, R. Zenobi, M. Niu
Separating Breath from Eructation: Advancing SESI-Based Breathomics in Dairy Cows
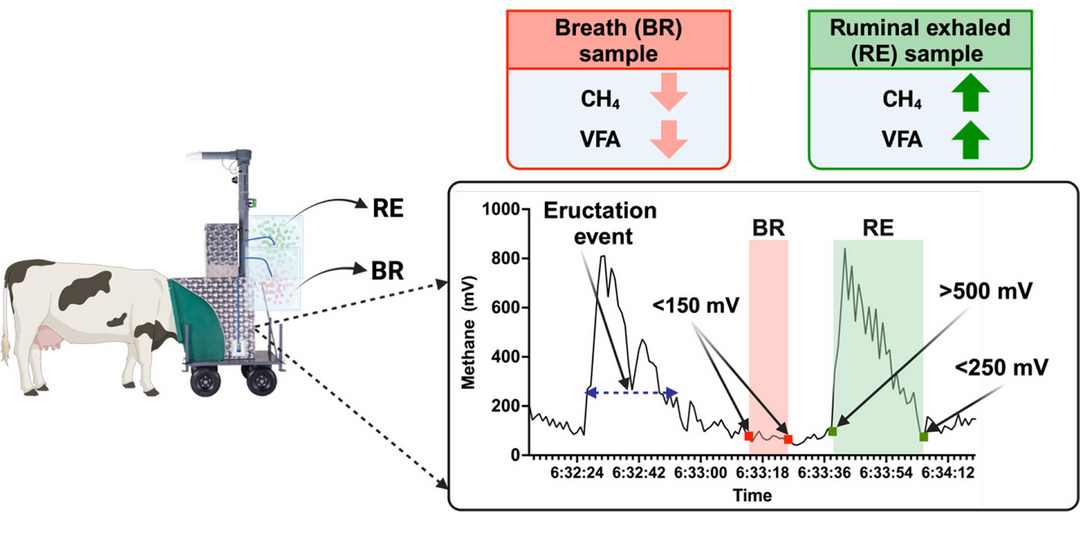
This study establishes a validated sampling method to distinguish true breath (BR) from ruminal eructation (RE) in dairy cows—an essential step for applying breathomics in ruminant metabolic research. Using a CH₄-based threshold and the GreenFeed system, researchers collected BR and RE samples from Holstein cows and analyzed them via SESI-HRMS and GC. CH₄ levels were 80% lower in BR, confirming successful separation. SESI-MS detected hundreds of VOC features, with distinct profiles between BR and RE. RE was enriched in VFAs like acetate and butyrate, while BR showed unique endogenous signals. This approach unlocks non-invasive, real-time breath metabolomics for metabolic phenotyping in ruminants, overcoming a long-standing barrier in the field.
Practical Applications of Secondary/ Extractive Electrospray Ionization (SESI): A Versatile Tool for Real‐Time Chemical Analysis
X.Luo, H. Wang, X. Hu, Sa. Gligorovski, X.Liu, P.Sinues
SESI and EESI: Two Decades of Real-Time Volatile Analysis
Since their resurgence during the ambient mass spectrometry revolution, secondary electrospray ionization (SESI) and extractive electrospray ionization (EESI) have transformed real-time analysis of gas and aerosol mixtures. Originally discovered in the 1980s, these techniques now underpin a wide range of applications—from drug detection to environmental monitoring and metabolomics. Over the past two decades, the field has seen rapid expansion, thanks in part to technological advances driven by innovators such as Fossiliontech (FIT). This review summarizes key milestones, showcases diverse applications, and outlines emerging opportunities and challenges.
Challenges in the identification and quantitation in on-line breath analysis
H. G. Mengers, F. Völker, L. M. Blank
Validating VOC Quantification in Breath: MS1 vs MS2 Approaches in SESI-MS
This study critically evaluates the accuracy of compound identification and quantification in SESI-MS breath analysis, comparing MS1-based methods to targeted MS2 techniques. Using C5–C10 aldehydes, limonene, and pyridine as known breath markers, researchers tested full scan, selected ion monitoring, and parallel reaction monitoring across 12 volunteers. While high-abundance VOCs like limonene and pyridine were reliably detected, low-abundance aldehydes posed significant challenges due to isomeric interference (e.g., from ketones), leading to misassignments—even with MS2. The study underscores the need for robust MS2 validation in SESI workflows to avoid false positives and ensure quantitative accuracy in clinical and diagnostic breath analysis.
Breath Analysis of Propofol and Associated Metabolic Signatures: A Pilot Study Using Secondary Electrospray Ionization–High-resolution Mass Spectrometry
J. Zeng, N. Stankovic, K. D. Singh, R. Steiner, U. Frey, T. Erb, P. Sinues
Breath Pharmacometabolomics of Propofol Anesthesia in Children
This pilot study demonstrates that on-site SESI-HRMS breath analysis can robustly track propofol and its metabolites in pediatric patients, with exhaled signals showing strong correlation to serum concentrations (R² ≥ 0.65). Beyond pharmacokinetics, SESI revealed surgery-induced metabolic responses, including elevated fatty aldehydes—markers of oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation. Conducted in children undergoing IV anesthesia, this work highlights real-time, non-invasive breath profiling as a promising tool for individualized anesthetic monitoring and metabolic assessment during surgery.
Urinary marker of oxidative stress in children correlates with molecules in exhaled breath
A. Gisler, K. D. Singh, A. Marten, F. Decrue, U. Frey, P. Sinues and J. Usemann
Real-time breath analysis via secondary electrospray ionization high-resolution mass spectrometry (SESI-HRMS) shows promise as a non-invasive tool for assessing oxidative stress. In a study involving 128 children (25 tobacco smoke-exposed, 103 non-exposed), 71 breath features significantly correlated with urinary levels of the oxidative stress marker 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α (8-iso-PGF2α). Breath analysis moderately predicted urinary 8-iso-PGF2α (concordance correlation: 0.37 ± 0.05), suggesting potential clinical applicability
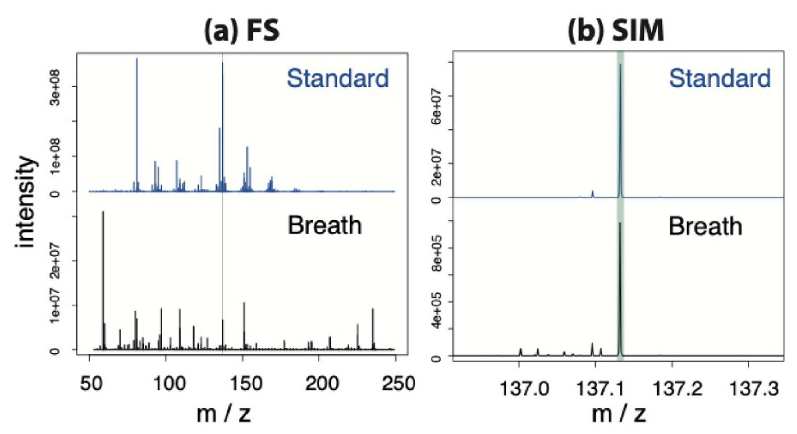
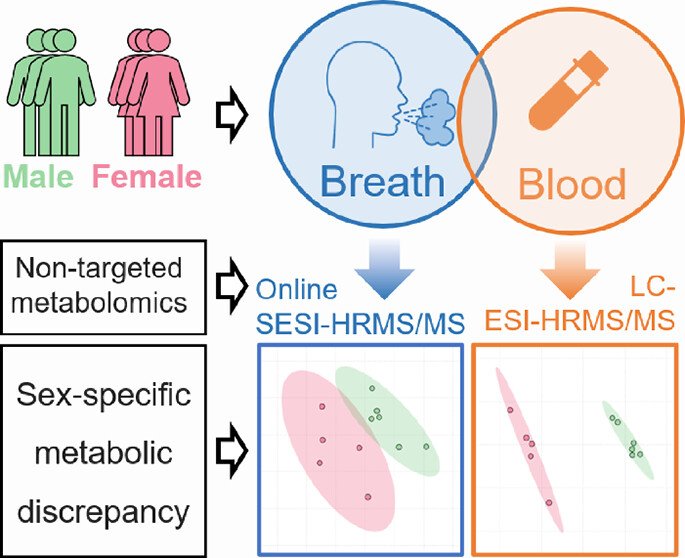
Breath and Blood Metabolomics: A Comparative Study Using SESI-HRMS/MS and UHPLC-ESI-HRMS/MS
Zhifeng Tang, Jianming Yang, Xin Xu, Keda Zhang, Huiling Wang, Xin Luo, Mingliang Fang, Tao Huan, Xue Li
Breath metabolomics enables noninvasive and rapid acquisition of metabolic information by detecting volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in exhaled breath. Secondary electrospray ionization high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry (SESI-HRMS/MS) offers the highest coverage for detecting breath metabolites among current real-time breath analysis techniques. Although it has been generally recognized that metabolites in breath originate from the blood, a molecular-level understanding of the characteristics of metabolites in both breath and blood remains insufficient. In this study, nontargeted analyses of breath and blood samples from 11 healthy volunteers were performed using SESI-HRMS/MS and ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography electrospray ionization high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-ESI-HRMS/MS), respectively…
Pain induces a rapid characteristic metabolic signature detectable in breath
P. Sinues, M. Richard, K. Singh, D. Sezer, S. Buergler, L. Palermo, Y. Schulz, Z. Tang, X. Luo, U. Frey, P. Cattin, X. Li, J. Gaab
Accurately assessing pain in vulnerable populations—such as children, the elderly, and unconscious patients—remains a critical challenge in healthcare. A new study explores the potential of breath metabolomics as a real-time, objective tool for pain evaluation. Using the cold pressor test (CPT) to induce pain, researchers analyzed exhaled breath with high-resolution mass spectrometry, identifying over 400 metabolic changes within 15 minutes. Key pathways linked to pain signaling, including amino acid metabolism and neurotransmitter activity, showed significant shifts. A neural network classifier effectively distinguished pre- and post-CPT states (AUC=0.856), highlighting the promise of this approach. These findings align with chronic pain research, suggesting a deeper metabolic connection to pain perception. This breakthrough paves the way for observer-independent pain monitoring, with future research needed to tailor insights for personalized pain management strategies.
Assessing asthma-specific breath markers in preschool children using remote breath collection
R. Bourgeois, K. Rohrbach, Y. Baumann, N. Perkins, E. Seidl, S. Micic, A. Moeller
Remote Breath Profiling of Preschool Asthma Using SESI-HRMS
This pioneering study demonstrates that SESI-HRMS combined with offline Nalophan-based breath collection can detect asthma-specific VOC markers in preschool children (ages 3–6). Out of 375 previously identified asthma-specific m/z features, 125 were re-detected, with 16 showing statistically significant differences between symptomatic patients and healthy controls. Several markers mapped to known metabolic pathways, and classification performance (AUC 0.77) confirms diagnostic potential. This is the first validation of SESI-based asthma diagnostics in young children using a remote, non-invasive method—a promising step toward early, accurate respiratory disease detection.
Rapid detection of Tulipalin A with SESI-Orbitrap MS: an exploration across spring flowers
Kim Arnold, Alejandro Gómez-Mejia, Miguel de Figueiredo, An N. T. Phan, Roy Eerlings, Hendrik G. Mengers & Lars M. Blank
Here, we demonstrated the secondary electrospray ionization coupled Orbitrap mass spectrometry (SESI-Orbitrap MS) methodology for quantifying tulipalin A release from plants upon injury.
Early detection of bacterial pneumonia by characteristic induced odor signatures
Kim Arnold, Alejandro Gómez-Mejia, Miguel de Figueiredo, Julien Boccard, Kapil Dev Singh, Serge Rudaz, Pablo Sinues & Annelies S. Zinkernagel
This study refines the application of the non-invasive Secondary Electrospray Ionization-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (SESI-HRMS) methodology for real-time and early detection of human respiratory bacterial pathogens in the respiratory tract of a mouse infection model
Molecular breath profile of acute COPD exacerbations
Sarah Basler, Noriane A Sievi, Felix Schmidt, Kai Fricke, Alexandra Arvaji, Jonas Herth, Diego M Baur, Pablo Sinues, Silvia Ulrich and Malcolm Kohler
Metabolic changes in the linoleate, tyrosine, and tryptophan pathways during AECOPD were predominant. Significant metabolic changes occur during COPD exacerbations, predominantly in the linoleate, tyrosine, and tryptophan pathways, which are all linked to inflammation. Real-time exhaled breath analysis enables a good prediction of AECOPD compared to stable state and thus could enhance precision of AECOPD diagnosis and efficacy in clinical practice.
Pharmacometabolomics via real-time breath analysis captures metabotypes of asthmatic children associated with salbutamol responsiveness
Jiafa Zeng, Jakob Usemann, Kapil Dev Singh, Anja Jochmann, Daniel Trachsel, Urs Frey, Pablo Sinues
Pharmacometabolomics via exhaled breath analysis holds promise for patient stratification. Here, we integrate a real-time breath analysis platform in the workflow of an outpatient clinic to provide a detailed metabolic snapshot of patients with asthma undergoing standard clinical evaluations. We observed significant metabolic changes associated with salbutamol inhalation within ∼1 h. Our data supports the hypothesis that sphingolipid metabolism and arginine biosynthesis mediate the bronchodilator effect of salbutamol…
Diagnostic potential of breath analysis – Focus on the dynamics of volatile organic compounds
Wolfram Miekisch, Pritam Sukul, Jochen K. Schubert
As dynamic VOC profiling provides valuable information on kinetics of markers and confounders, it offers huge and so far unexplored potential for physiological, metabolic, therapeutic and environmental monitoring. Driven by new and innovative technologies such as real time mass spectrometry and highly specific sensor systems, future applications may range from home care to ICU monitoring
Ozone Oxidation of the Flame Retardant BDE-209: Kinetics and Molecular-Level Analysis of the Gas-Phase Product Compounds
Siyu Liu, Jinli Xu, Yingxin Xie, Bowen He, Qingxin Deng, Yanan Hu, Jiangping Liu, Davide Vione, Xue Li, Sasho Gligorovski
Real-time measurements of the gas-phase product compounds formed by the reaction of O3 with BDE-209 were performed with a SESI-HRMS in both positive and negative ionization modes…