Challenges in the identification and quantitation in on-line breath analysis
T. Käser, S. Giannoukos and R. Zenobi
Abstract
Validating VOC Quantification in Breath: MS1 vs MS2 Approaches in SESI-MS
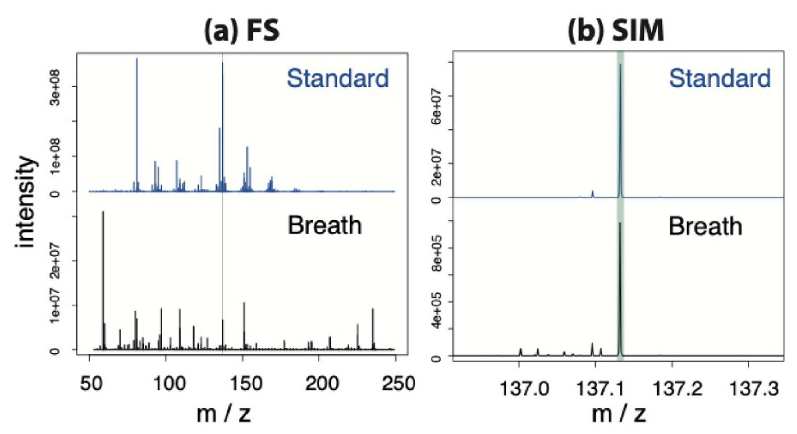
This study critically evaluates the accuracy of compound identification and quantification in SESI-MS breath analysis, comparing MS1-based methods to targeted MS2 techniques. Using C5–C10 aldehydes, limonene, and pyridine as known breath markers, researchers tested full scan, selected ion monitoring, and parallel reaction monitoring across 12 volunteers. While high-abundance VOCs like limonene and pyridine were reliably detected, low-abundance aldehydes posed significant challenges due to isomeric interference (e.g., from ketones), leading to misassignments—even with MS2. The study underscores the need for robust MS2 validation in SESI workflows to avoid false positives and ensure quantitative accuracy in clinical and diagnostic breath analysis.