Acute COPD exacerbation despite triple inhaled therapy: a molecular insight – TripleEx study
N.A. Sievi, F. Schmidt, K. Fricke, D.M. Baur, S. Basler, J. Herth, M. Kohler
Abstract
Breath metabolomics in COPD exacerbations
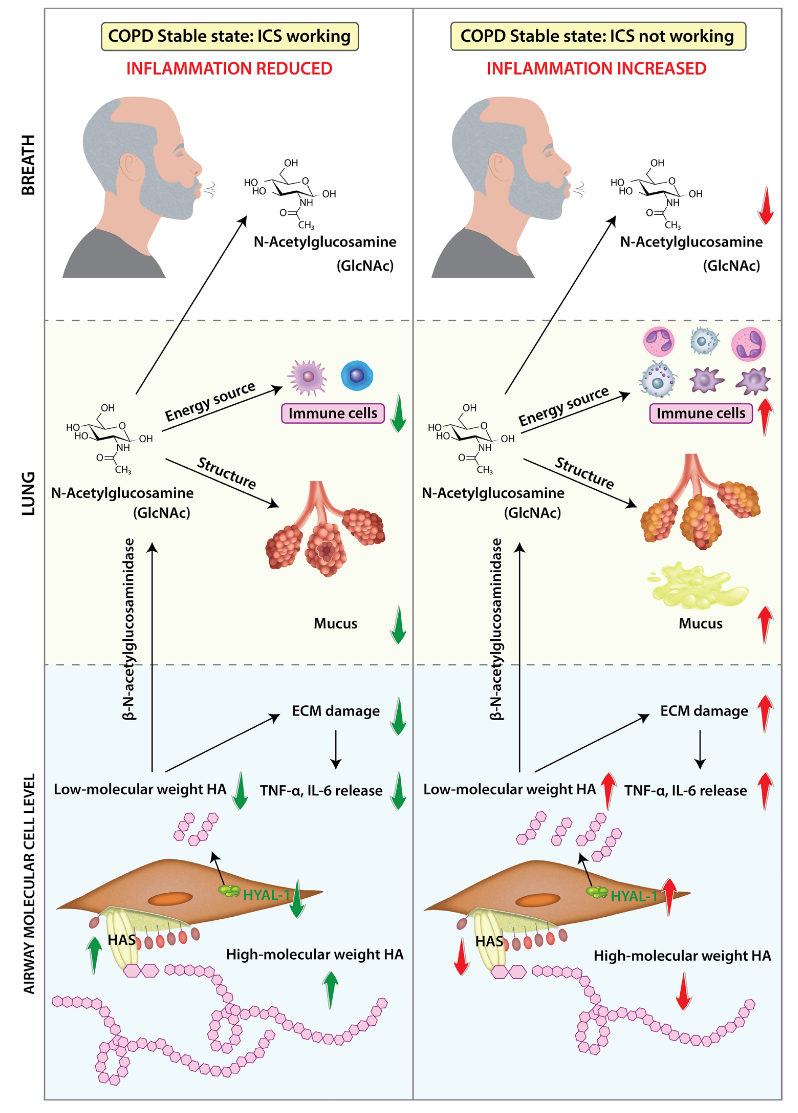
This study examined whether real-time breath analysis can detect metabolic changes during acute exacerbations of COPD (AECOPD) compared to the stable state in patients receiving triple inhaled therapy. Breath profiles from 28 patients revealed alterations in aminosugar, linoleate, and butanoate pathways. A prediction model discriminated AECOPD from stable state with high accuracy (AUC = 0.84, sensitivity and specificity 86%). These findings suggest that exhaled breath analysis may provide a rapid, non-invasive tool for detecting exacerbations and reveal aminosugar metabolism as a potential therapeutic target.