Gauging circadian variation in ketamine metabolism by real-time breath analysis
P. M-L Sinues, M. Kohler, S. A. Brown, R. Zenobi and R. Dallmann
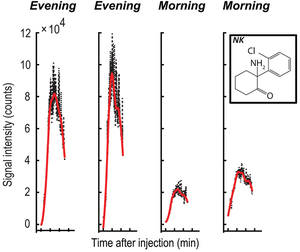
Abstract: The time-of-day of drug application is an important factor in maximizing efficacy and minimizing toxicity. Real-time in vivo mass spectrometric breath analysis of mice was deployed to investigate time-of-day variation in ketamine metabolism. Different production rates of ketamine metabolites, including the recently described anti-depressant hydroxynorketamine, were found in opposite circadian phases. Thus, breath analysis has potential as a rapid and 3Rs (Replacement, Reduction and Refinement) conforming screening method to estimate the time-dependence of drug metabolism.