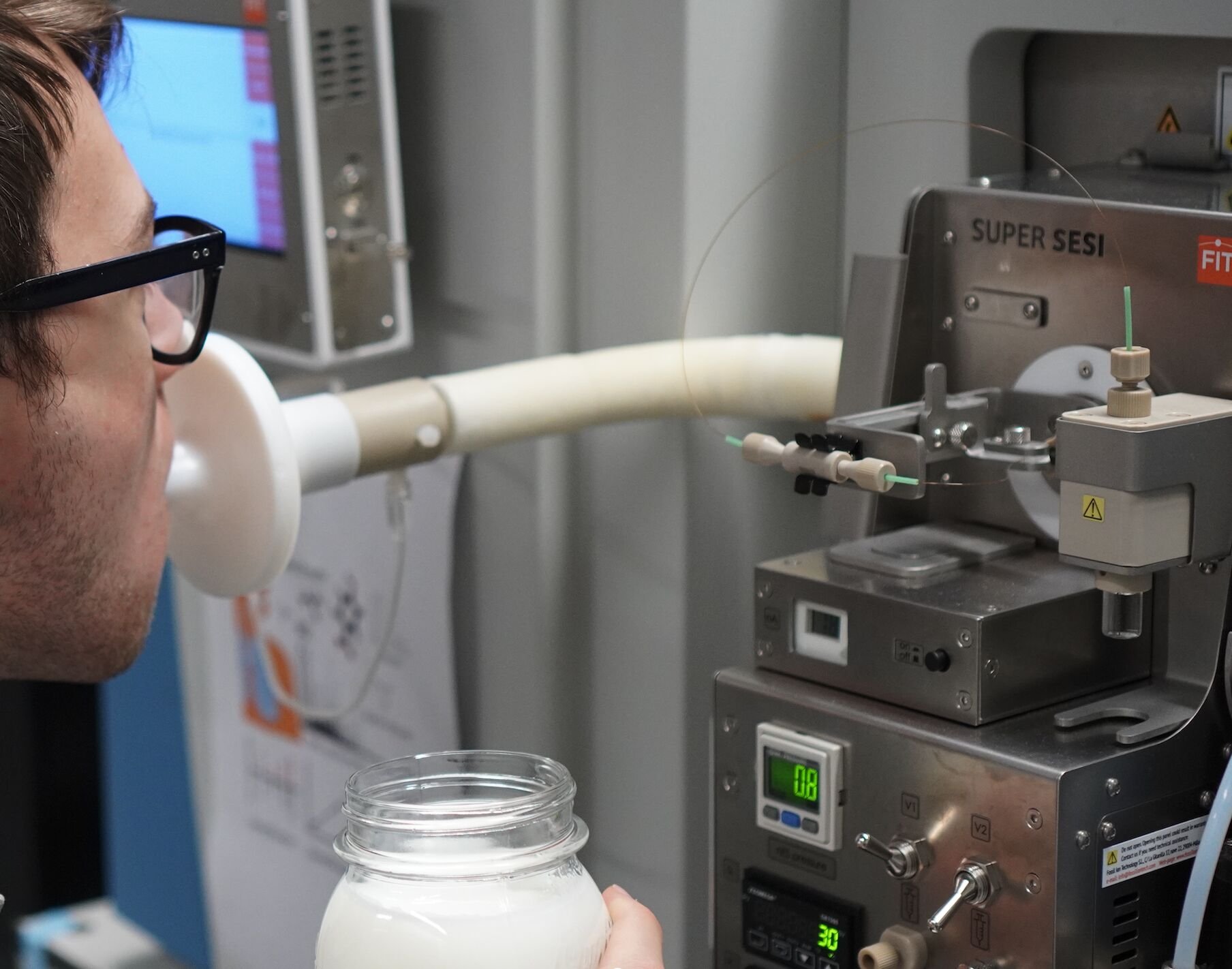
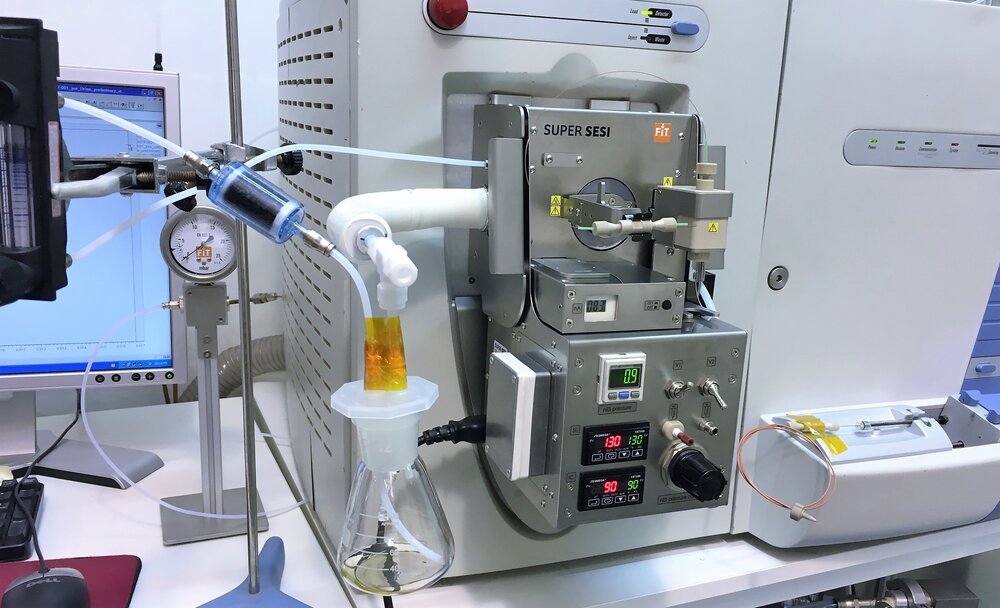
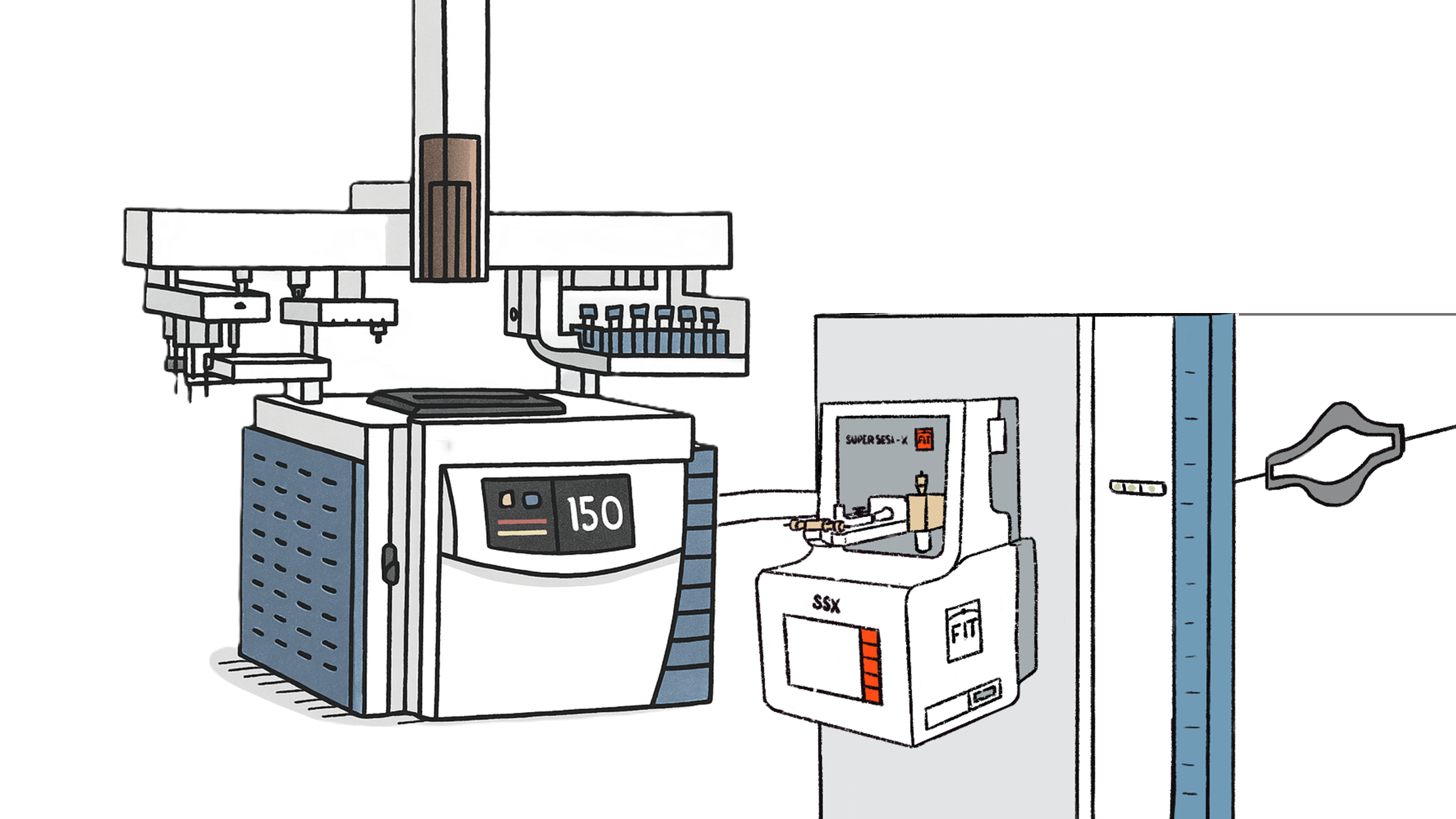
Volatilomics & Proteomics Ionization
Super Soft Electrospray Ionization delivers
clean spectra and reproducible results
from Breath Analysis to Top-Down Proteomics.
Clinical
Biomarker identification, Dosage optimization
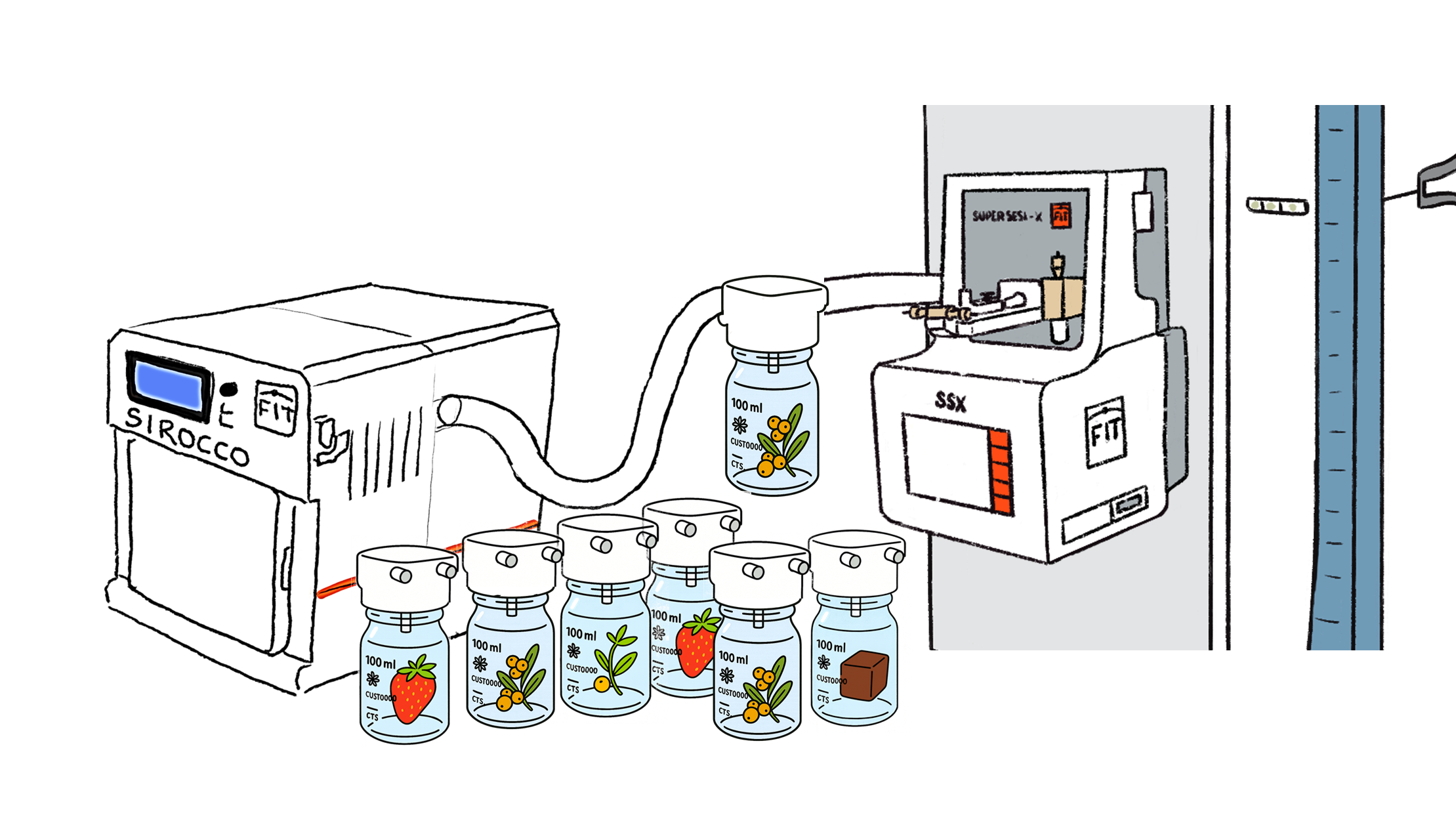
Food & Aroma
Control what makes your product a success.
Elite Sports
Prevent injuries,
optimize performance
Defense
Combat Readiness, Threat Trace Detection
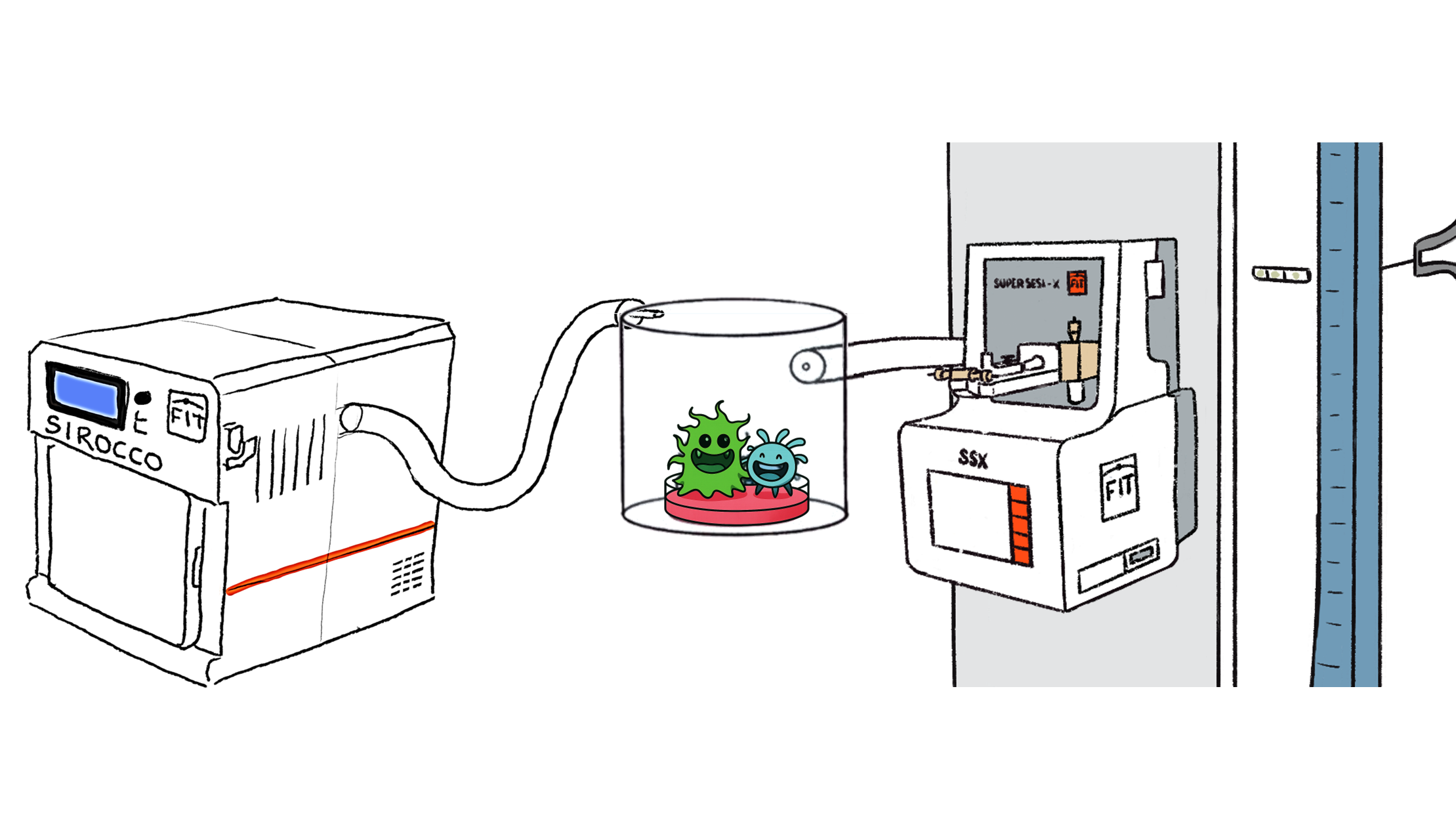
Microbiology
Real-time metabolomics, biorreactor monitoring
Pharma
Animal models, PK profiling, metabolic profiling.
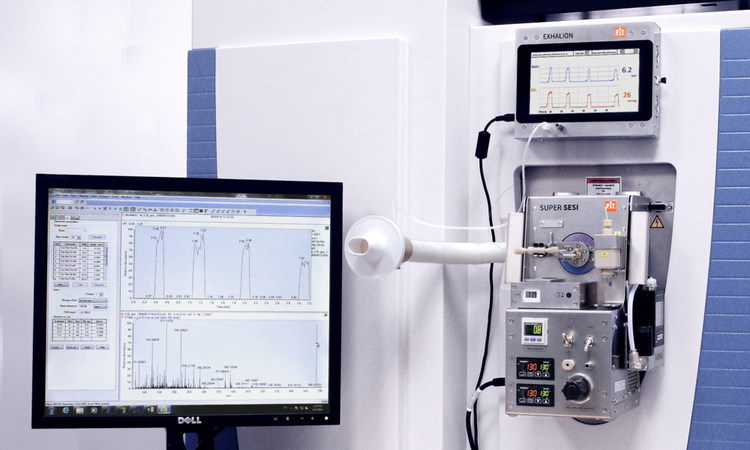
Volatilomic Applications
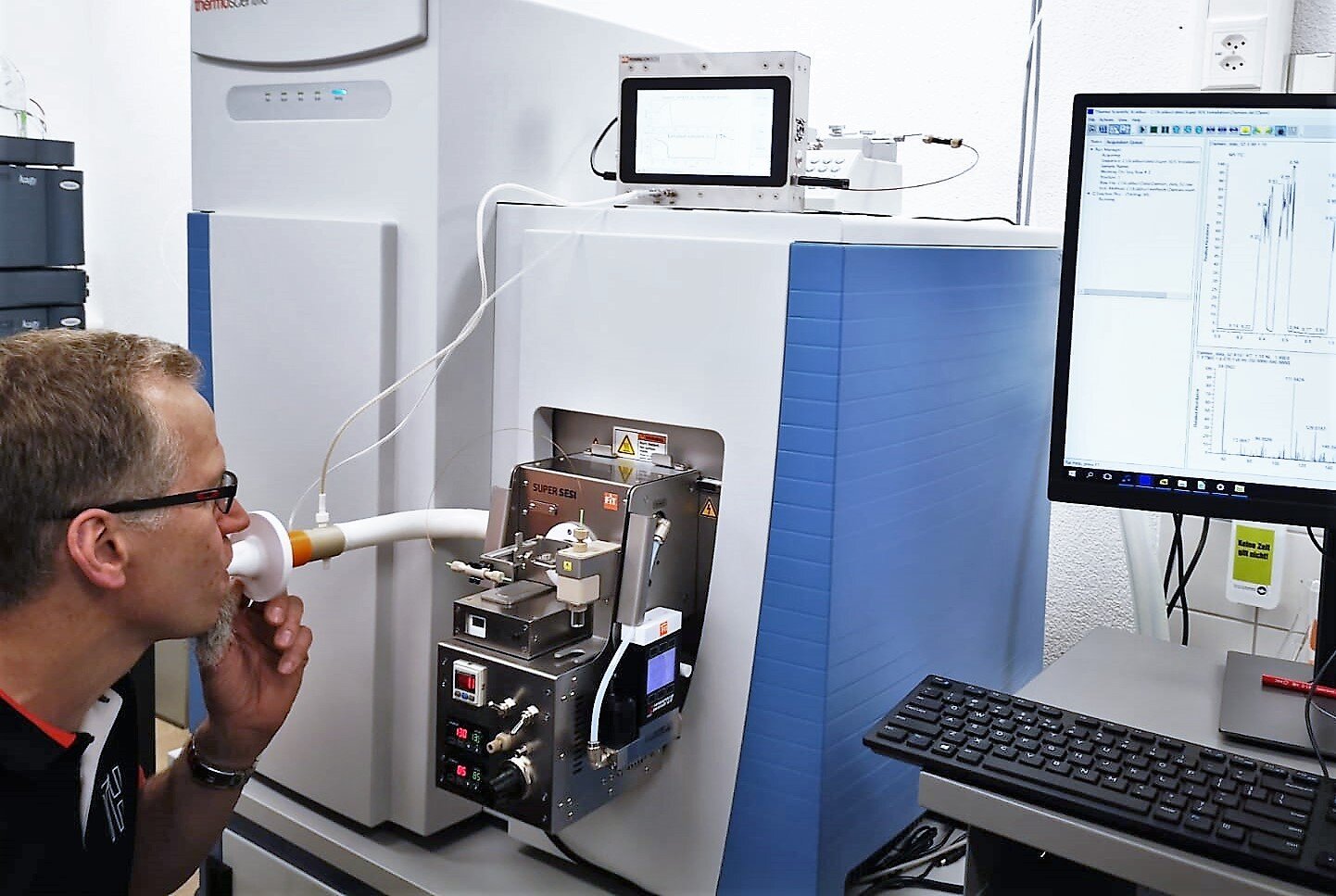
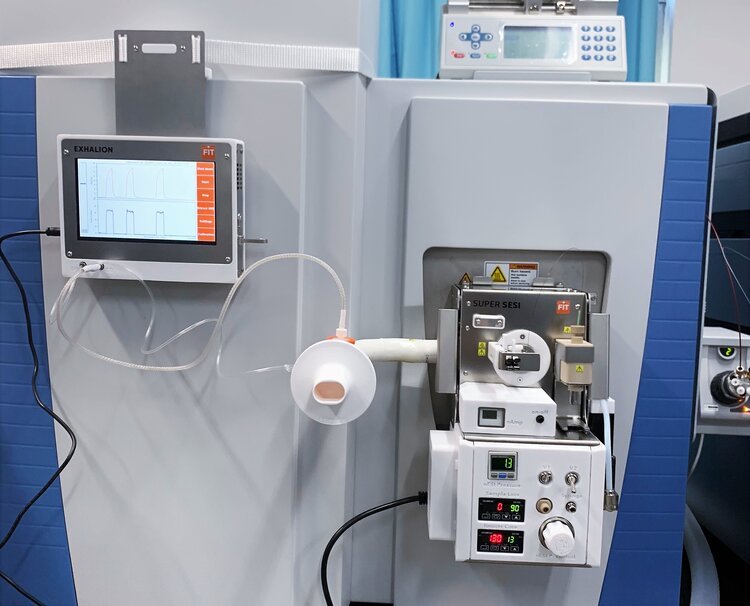
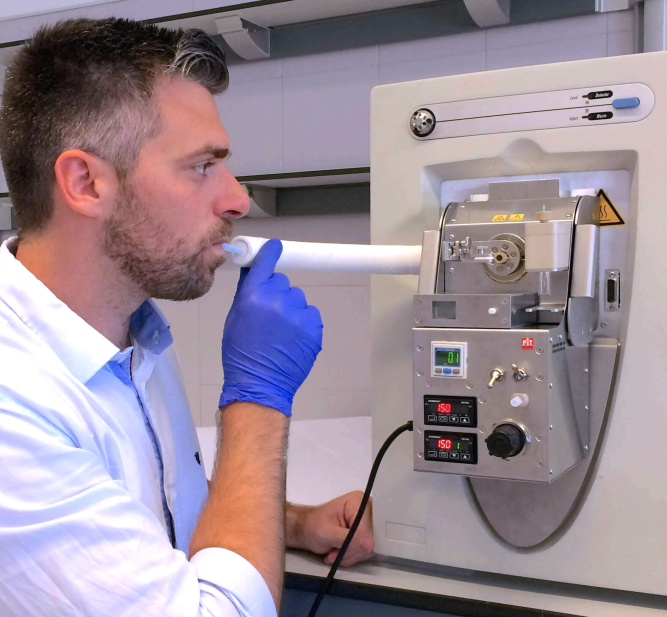
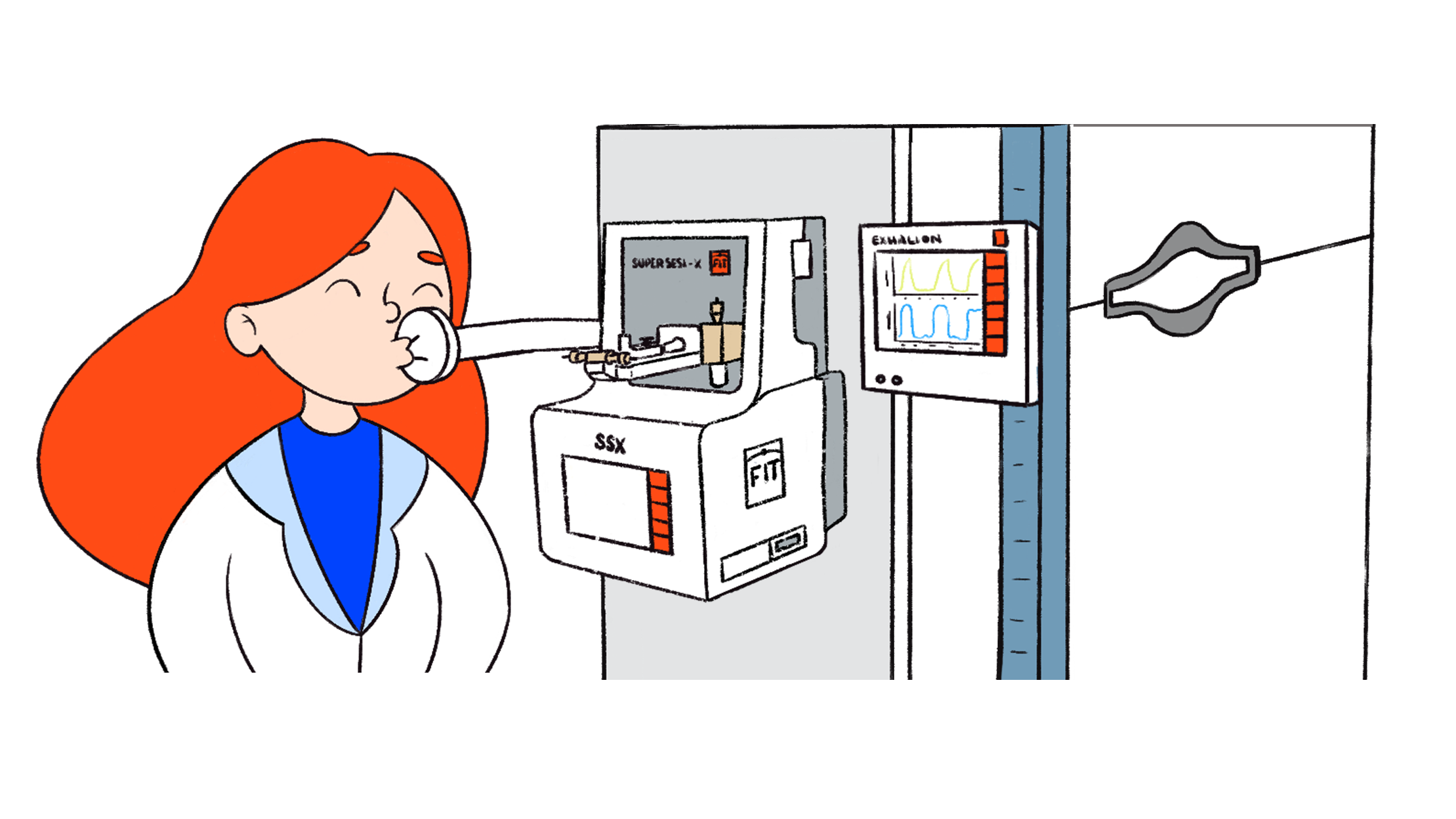
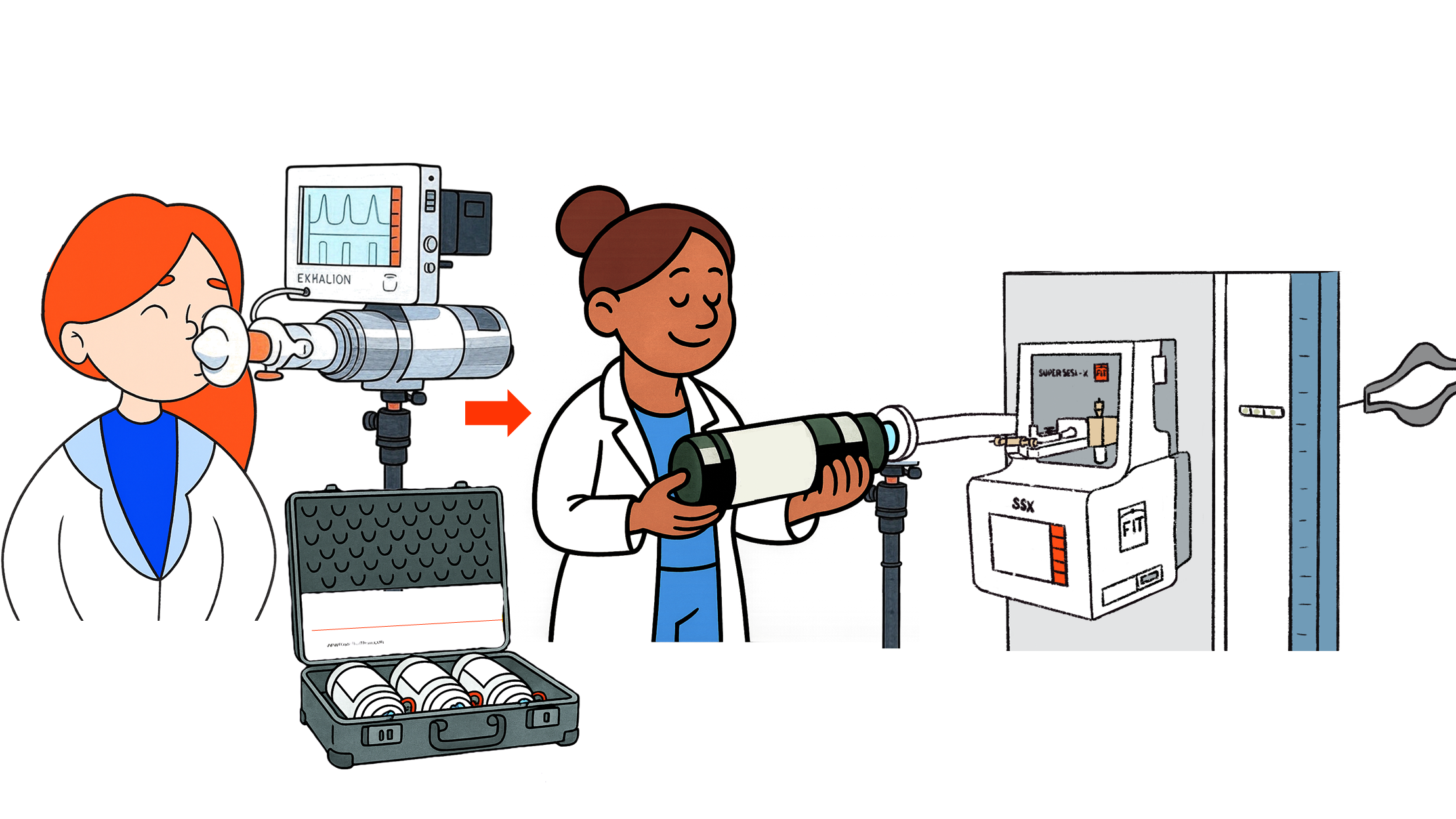
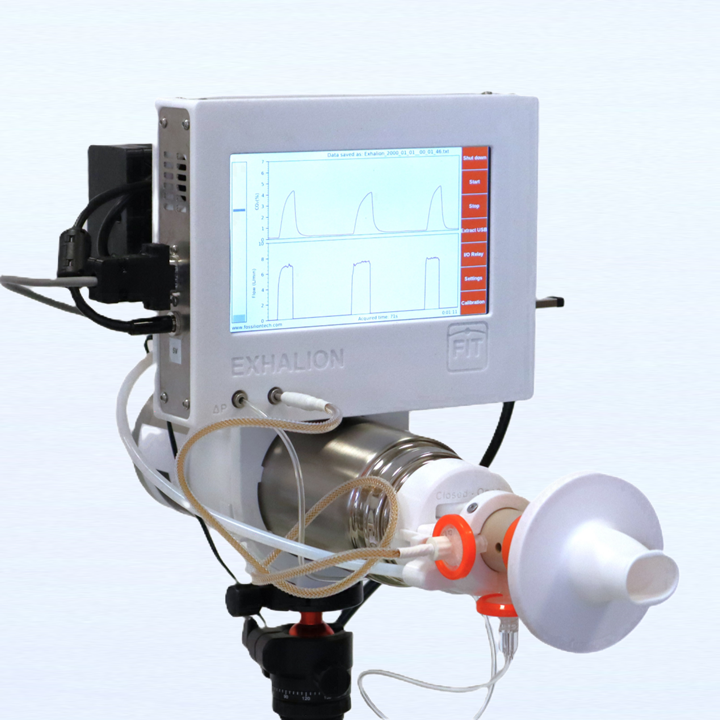
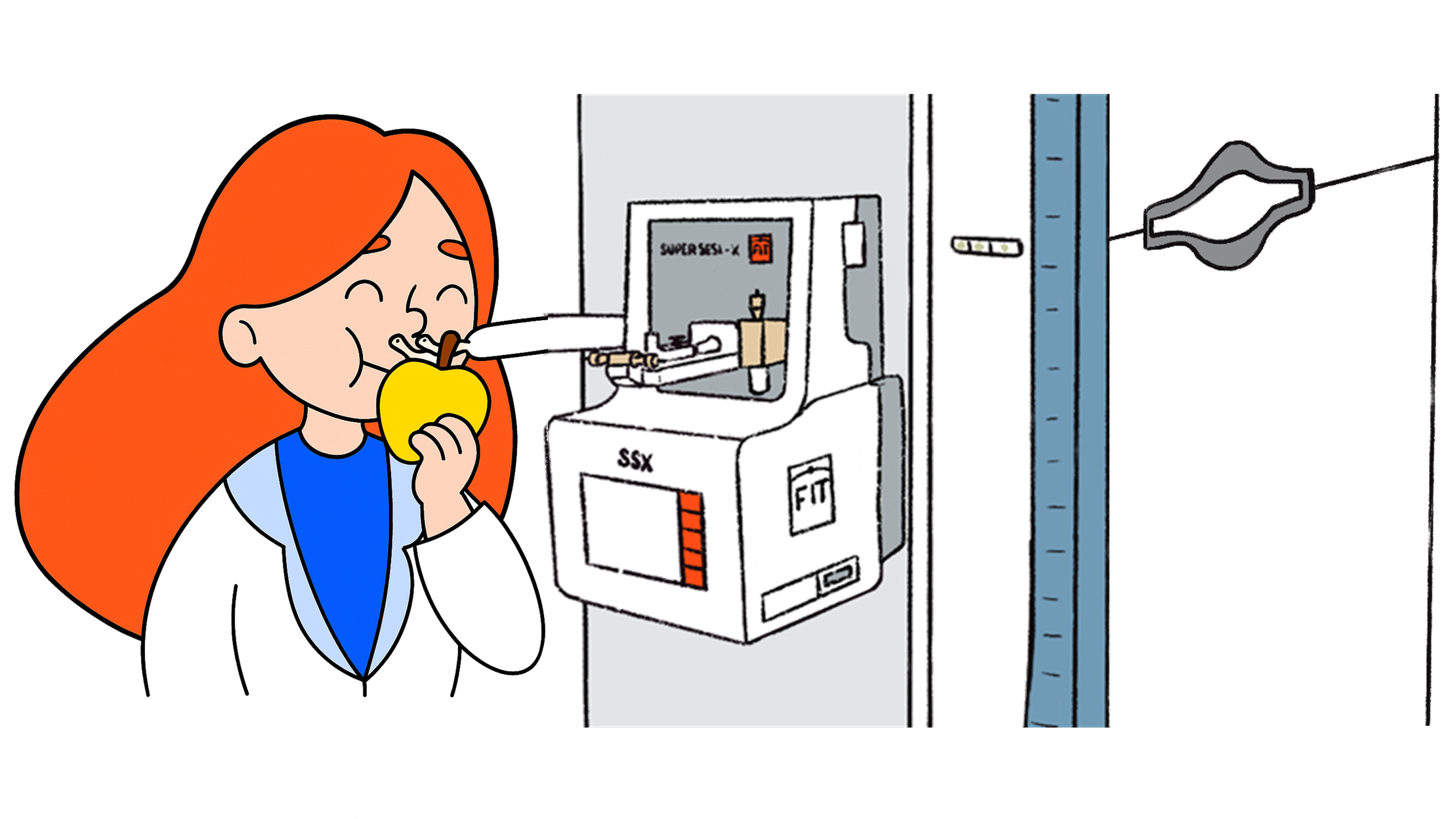
Breath analysis in real time
Dynamic Headspace Analysis
Breath analysis Offline
Headspace High throughput
Nose-space analysis
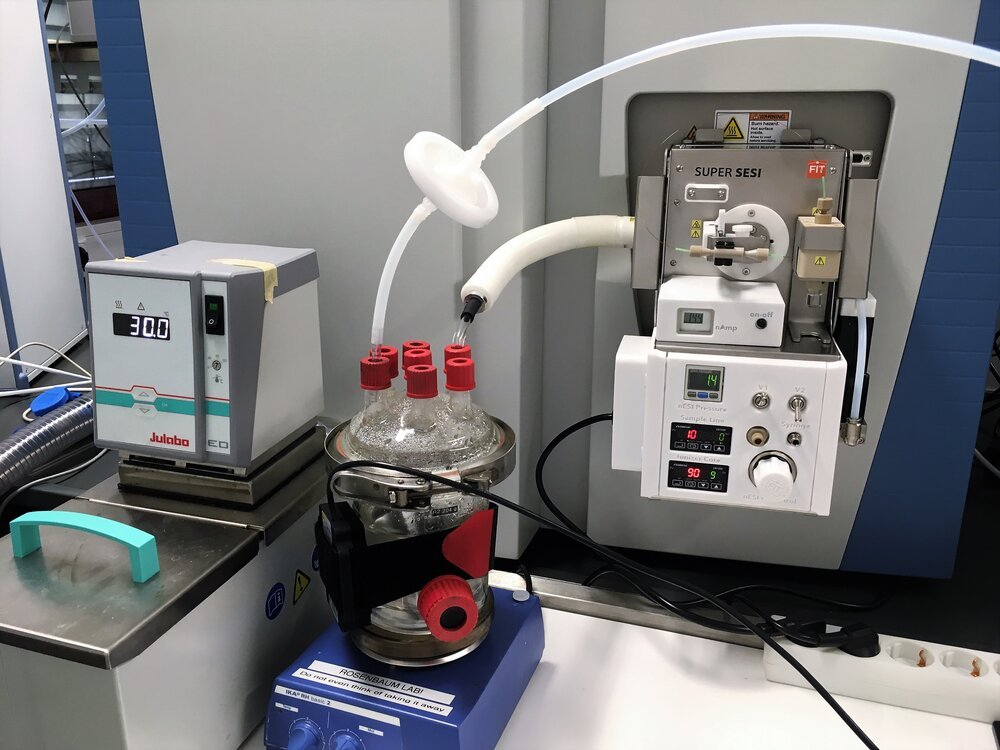
SUPER SESI, EXHALION,
Nose-space adaptor
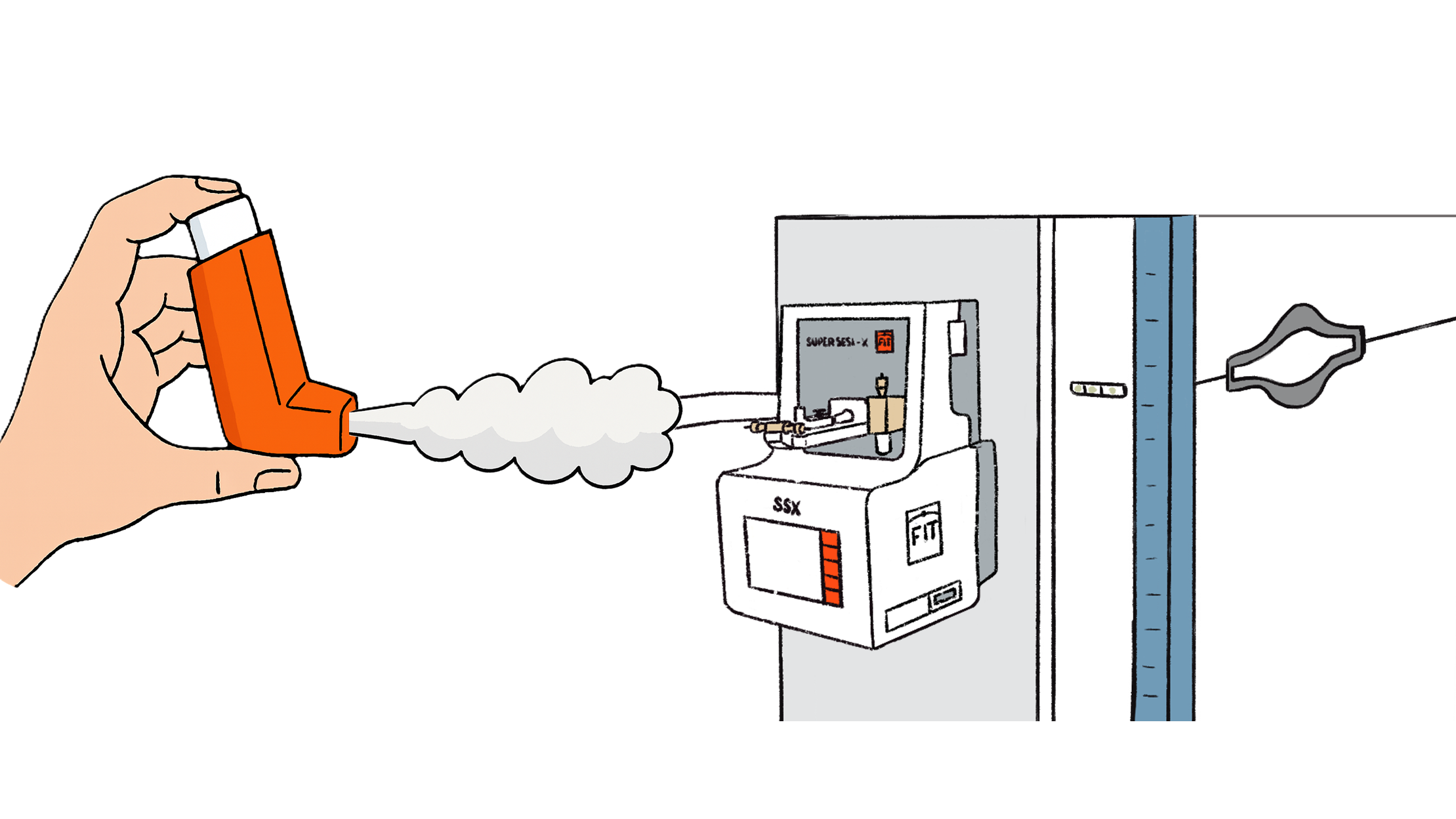
Aerosol and smoke analysis
SUPER SESI,
Aerosol adaptor
Offline Trace detection
GC - SESI -MS
SUPER SESI,
GC adaptor
Electrospray provides the best data, but it’s twitchy, demanding, and unforgiving. And when you're working with complex biological samples, the stakes are even higher. We build tools that take that raw power and make it usable.
From hospitals and food labs to proteomics core facilities, a reliable electrospray gives you statistically significant data you can trust to:
Measure intact proteins
Find biomarkers hiding in breath, plasma, or tissues
Decode flavor, freshness, and spoilage with chemical clarity
Monitor exposure in air, on-site, or in real time
Skip the chromatography and get faster answers with less prep
Need emitters?
We make them on demand: LOTUS, Classic and HALO.
Freshly built and shipped within 7 business days.
Customer reviews:
FIT emitters (proteomics):
BC Cancer Research Centre (Canada) - Selfpack Dragonfly nano-Column with LOTUS emitter
“Overall, we are very happy with the performance of the LOTUS (Dragonfly) columns. They pack very easily and are extremely stable. This latter aspect is probably the best part about them, the tip performance never seems to degrade. Usually with self-pulled emitters, the tip performance will degrade after 100 injections or so in my experience. The first column I packed in the LOTUS emitter column lasted for over 1000 injections without a drop in performance (and this wasn't continuous usage either, it was uninstalled and reinstalled many times). The only reason I stopped using that one actually was it looked like the capillary around the column-emitter junction was starting to become a bit worn out and I was worried it was going to break, but the tip itself was still fine”.
Acoustica Bio (USA) - LOTUS emitters ref. 50-05 and 30-05.
“The emitters worked great! Congrats on your products – they are very well made.“
The Kennedy Group - University of Michigan (USA) - 20 μm ID with a flow rate of 250-750 nL/min.
“We use The Sharp Singularity nano-ESI emitters with our Q-Tof Premier Mass Spectrometer from Waters. They are working really well for us. The spray stability we can reach with them is better than with other brands we have tried in the past!"
Universitätsspital Zürich, USZ (Switzerland) - 20 μm ID
"Our group has been using FIT's products since many years ago, and we're very happy with them! The nano-ESI emitters The Sharp Singularity are working great with our Orbitraps. The first time we tried them we had some issues, but after a videocall with Guillermo (FIT's CTO) he gave us some tips and everything was solved"
Max-Planck-Institut für molekulare Zellbiologie u. Genetik (Germany) - 20 μm ID with a flow rate of 400-500 nL/min.
“We are very happy with "The Sharp Singularity" nano-ESI emitters. We work in proteomics, and we use them with all the Orbitraps in the lab. We have no bad words about them! They are very robust.”
Department of Infectious Diseases & Immunology - University of Florida (USA) - 20 μm ID with a flow rate of 180-300 nL/min.
"We have been using them with our Q-tof, and we are very happy with them. We had to get used to them because we were using pulled emitters before, but after using them for some time everything worked really well!"
Fondazione IRCCS - Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori (Italy) - 20 μm ID
"We are using the nano-ESI emitters The Sharp Singularity in our latest project and they are working very well. We use them 5 days a week, 5 hours per day, and the results are being very good! They seem cleaner than the New Objective ones we were using before"
National Research Council Canada (Canada) - 30 μm ID
"FIT's nano-ESI emitters are working very well for our experiments!"
Uniwersytet Gdański (Poland) - 10 μm ID with a flow rate of 300 nL/min.
“These nano-ESI emitters are working great for our research in peptidomics. We use them with our Orbitrap Exploris 480, and we are very satisfied with them.”
Super SESI:
Dr. Prof. Patrik Španěl - J. Heyrovsky Institute of Physical Chemistry of the CAS, Prague, Czech Republic
“The SSX ion source is surely a masterpiece of state of the art engineering. Full understanding of the ion chemistry occurring between the ESI generated ions and VOC molecules inside will be an interesting challenge to tackle.”
Prof. Dr. med. Malcolm Kohler - University Hospital Zurich (USZ), Switzerland.
“We observed significant changes in glyoxylate and dicarboxylate, tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA), and tryptophan metabolic pathways. Our findings suggest that continuous monitoring of metabolite shifts from exhaled air should focus on monitoring platforms dedicated to volatile and slightly volatile metabolites”
Dr. Prof. Pablo Sinues - University Children’s Hospital Basel, University of Basel, Switzerland
“We use SESI-HRMS to sense exhaled molecules at minute concentrations. Since the analysis requires no sample-preparation or manipulation, the diagnostic result can be obtained nearly in real-time. This technology is especially well suited for children due to its non-invasive nature”
Dr. Prof. Jangjiang Zhu - The Ohio State University, Ohio, USA.
“Our results suggested that the optimized SESI-HRMS method can be suitable forthe analysis of VFAs from gut microbes in a rapid, sensitive, and non-invasive manner.”
Dr. Prof. Renato Zenobi - ETH Zurich, Switzerland
“When SESI is combined with state-of-the-art mass spectrometers, low limits of detection (pptv) are achievable without any sample pre-concentration. We exploit this feature in our lab in a number of projects which require fast mass spectrometric analysis of vapors at trace concentrations.”
Dr. Prof. Xue Li - Jinan University, Guangzhou, China.
“IAV infection induces a cascade of metabolite alterations, some of which are excreted via the skin and breath to the ambient air. Such IAV-induced odor traits could be captured by SESI-HRMS by simply dragging the air surrounding the infected mice into the analyzer. The process is non-invasive and rapid, as it requires no sample manipulation.”
Curious about electrospray?
Learn about ionization, proteomics, and volatilomics in a clear, hands-on way.
We break it down in our YouTube series, Playing with ions
How electrospray ionization works. Part 1
How electrospray ionization works, Part 2: setting the voltage.
How electrospray ionization works, Part 3: Why the emitters have to be so small?
Some tips to use the SUPER SESI QE
“Electrospray is a temperamental creature: The unicorn of electro-microfluidics: powerful, exquisitely sensitive, but unforgiving… Our mission is to tame the beast and turn electrospray into a dependable tool for everyday science.”
Trusted by Scientists around the world !