Detection of Escherichia coli via VOC Profiling using Secondary Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry (SESI-MS)
J. Zhu, J. E. Hill
Abstract: Escherichia coli O157:H7 (EC O157:H7), as well as its recently emerging non-O157 relatives, are a notorious group of pathogenic bacteria associated with foodborne outbreaks. In this study, we demonstrated that secondary electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (SESI-MS) could be a rapid and accurate detection technology for foodborne pathogens.
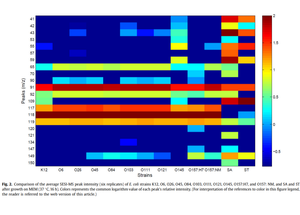
With SESI-MS volatile organic compound (VOC) profiling, we were able to detect and separate a group of eleven E. coli strains from two major foodborne bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella Typhimurium in three food modeling media. In addition, heatmap analysis of relative peak intensity show that there are six core peaks (m/z of 65, 91, 92, 117, 118 and 119) present and at a similar intensity in all eleven E. coli strains at the experimental conditions we tested.
These peaks can be considered conserved VOC biomarkers for E. coli species (robustly produced after just 4 h of growth). Bacterial strain-level differentiation was also attempted via VOC profiling, and we found that EC O157:H7 and EC O145 were differentiable from all other EC strains under the conditions investigated.